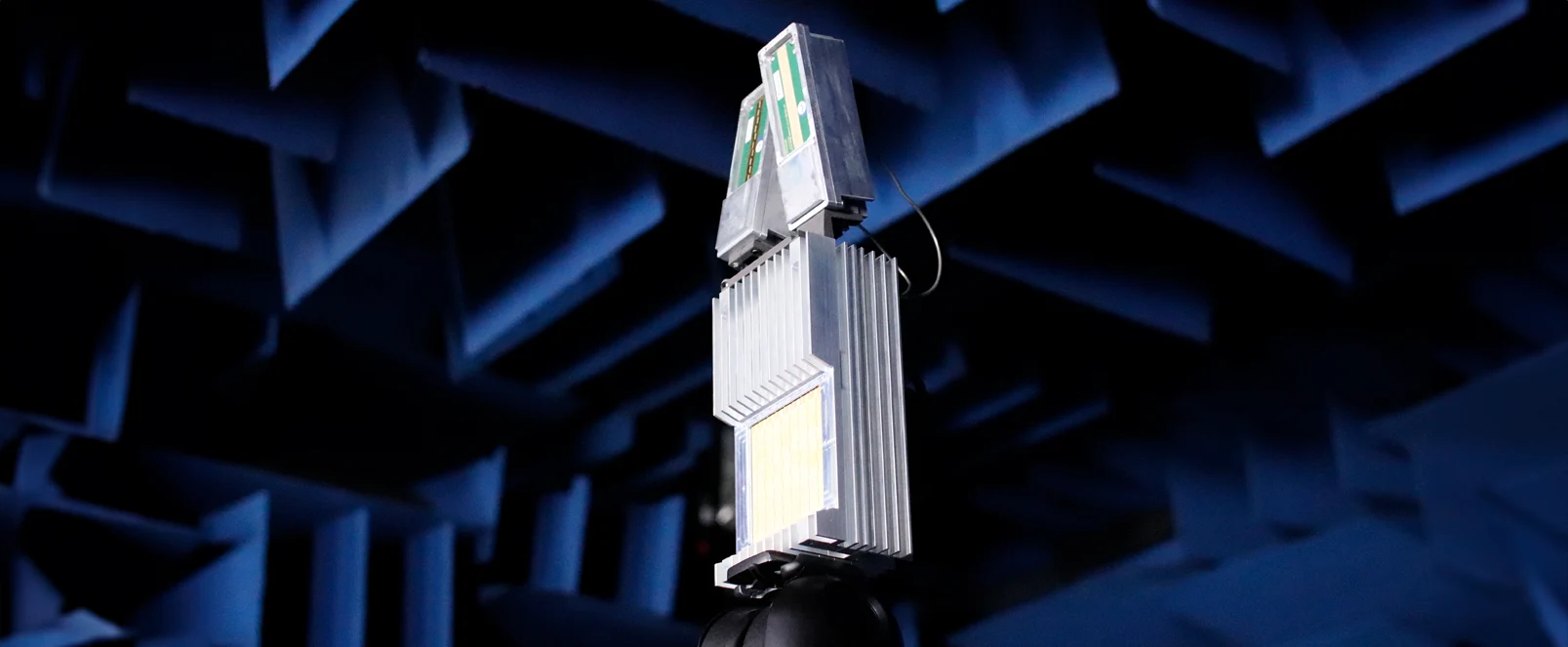
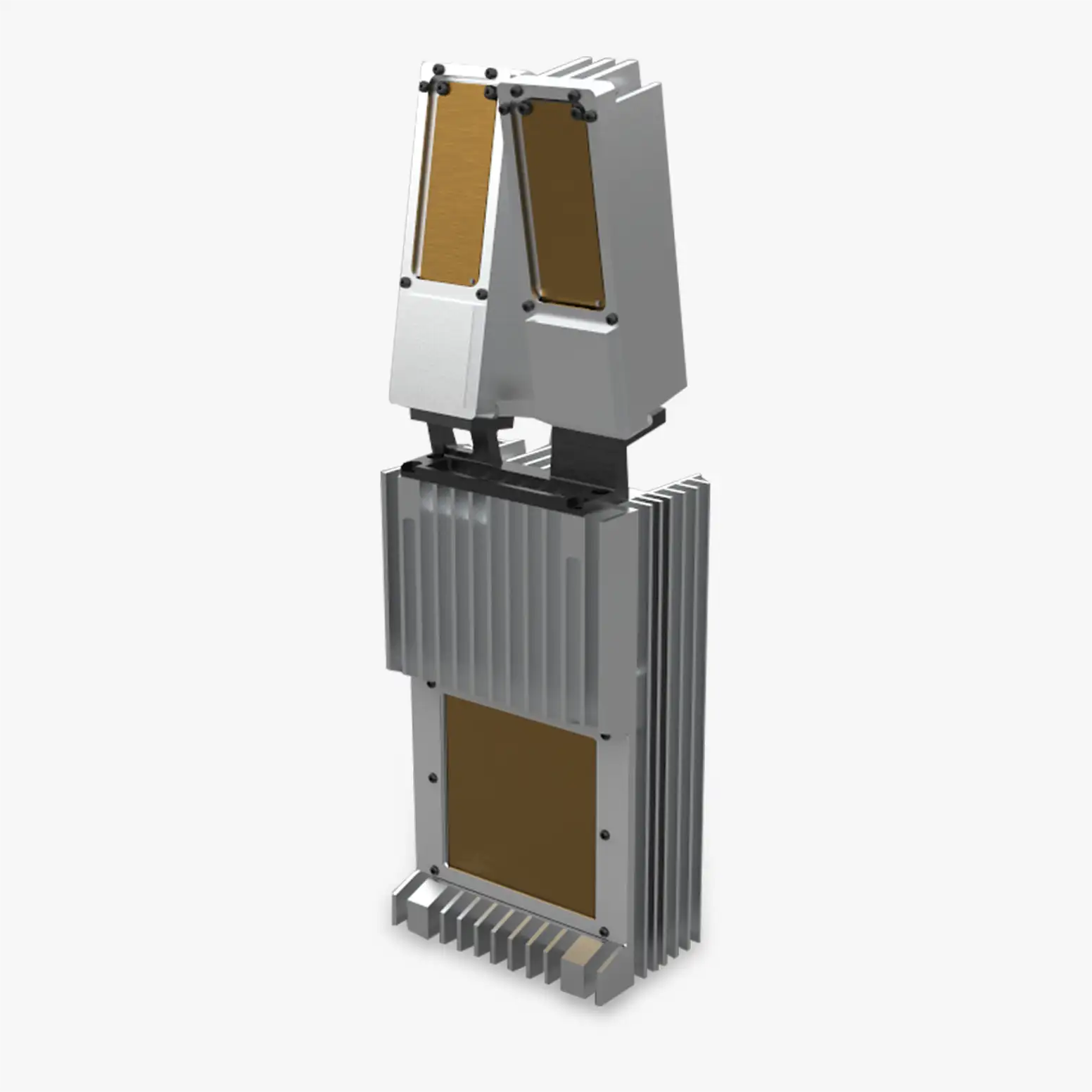
PLX-U16 Ubiquitous Radar
Detect, track and classify multiple targets across the entire field of view, with the ability to recognise birds, drones, people, vehicles and vessels via micro-Doppler analysis.
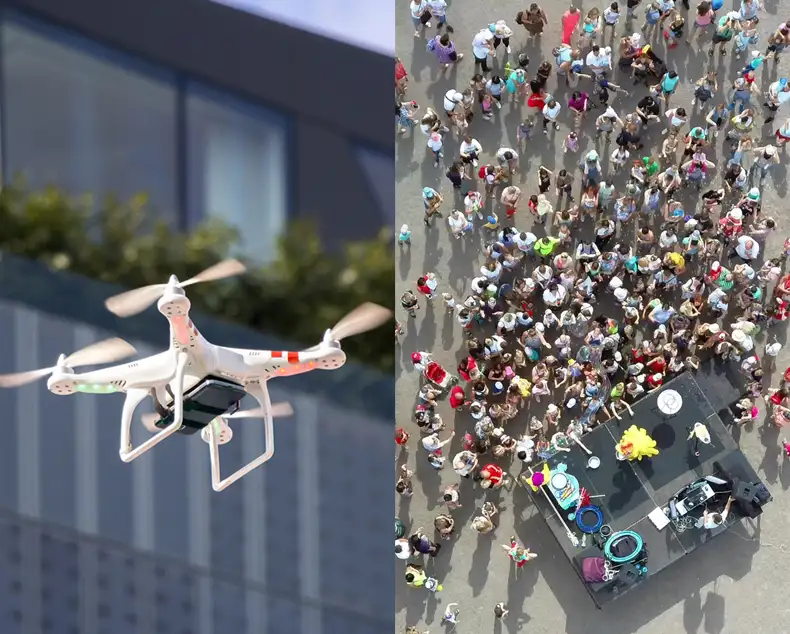
Drones and other unmanned aerial vehicles are now widely available in commercial, industrial and consumer markets. Reliably detecting, tracking and identifying drones can be problematic particularly in urban areas where line of sight is diminished.
Our Ubiquitous Radar has been designed and developed to address these issues. In contrast to traditional scanning radars which scan a narrow beam around the scene the PLX-U16 Radar is able to detect returns from many directions simultaneously. It can differentiate between drones and birds even determining the size and type of drone (e.g. fixed wing vs rotary wing).
The PLX-U16 has a wide range of applications and is very versatile, for example it can be deployed in congested environments (e.g. on ground, side of buildings) as part of a distributed sensing system. Alternatively, it can be mounted on drone/helicopter as a forward-facing radar to provide medium range (500 m – 1 km, depending on target size) detection.
Key features
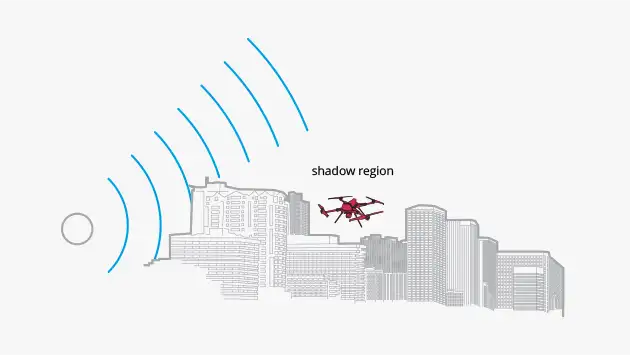
Background – Detecting UAS
- Countering drones is a difficult and challenging problem
- Detecting Class 1 drones at range is difficult (even with a high power radar)
- Class 1 drones can have a low RCS (-20 dBsm), and fly low and slow
- Ranges > 500 m difficult in many environments due to line of sight issues
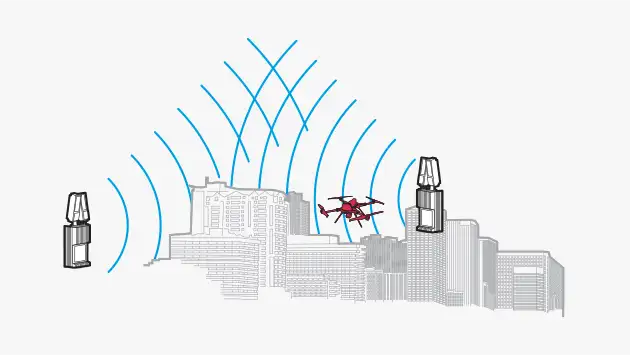
PLX-U16 – Distributed Sensing
- Use several radars to provide a distributed sensing capability
- Provides coverage in shadow regions
- Can deploy as unattended sensors to extend the range and area of coverage
Ubiquitous Radar Benefits

- Wide beam on transmit, digitally beamform on receive
- Radar able to detect returns from many directions simultaneously
- Contrast with traditional scanning radars which scan a narrow beam around the scene
- Enables tracking of multiple dynamic targets simultaneously
- Enables extended dwell times on a target which aids target classification, without compromising simultaneous wide area coverage
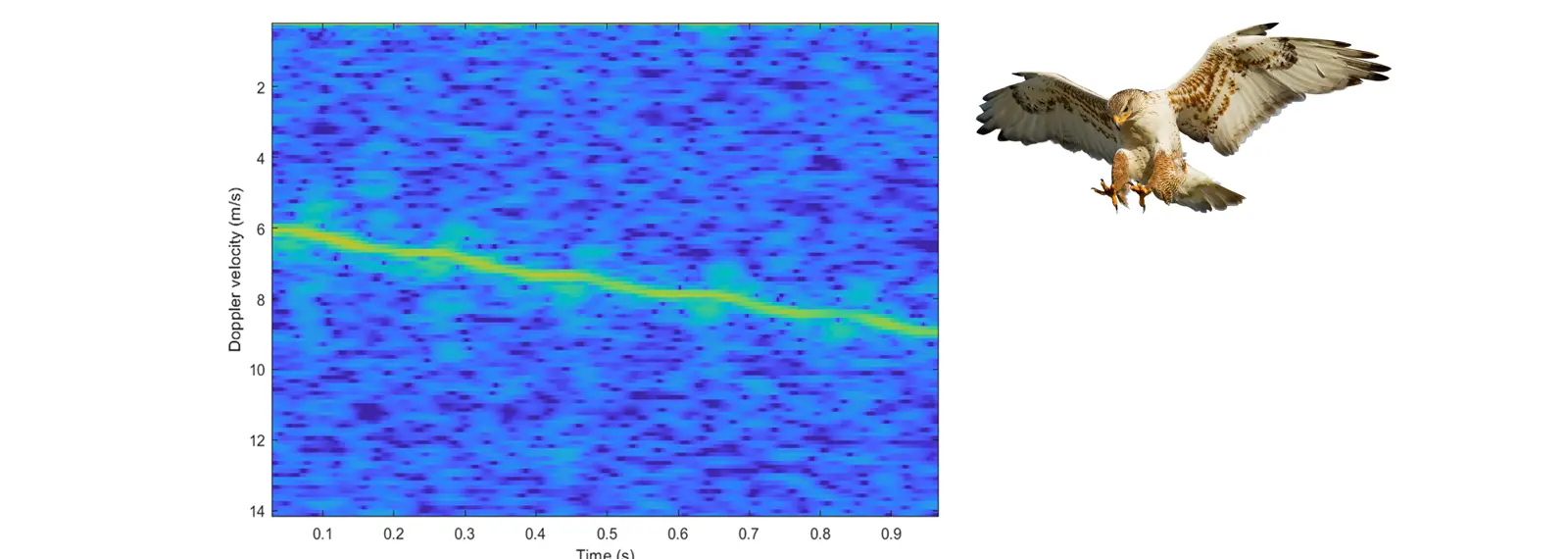
Target Classification: Bird
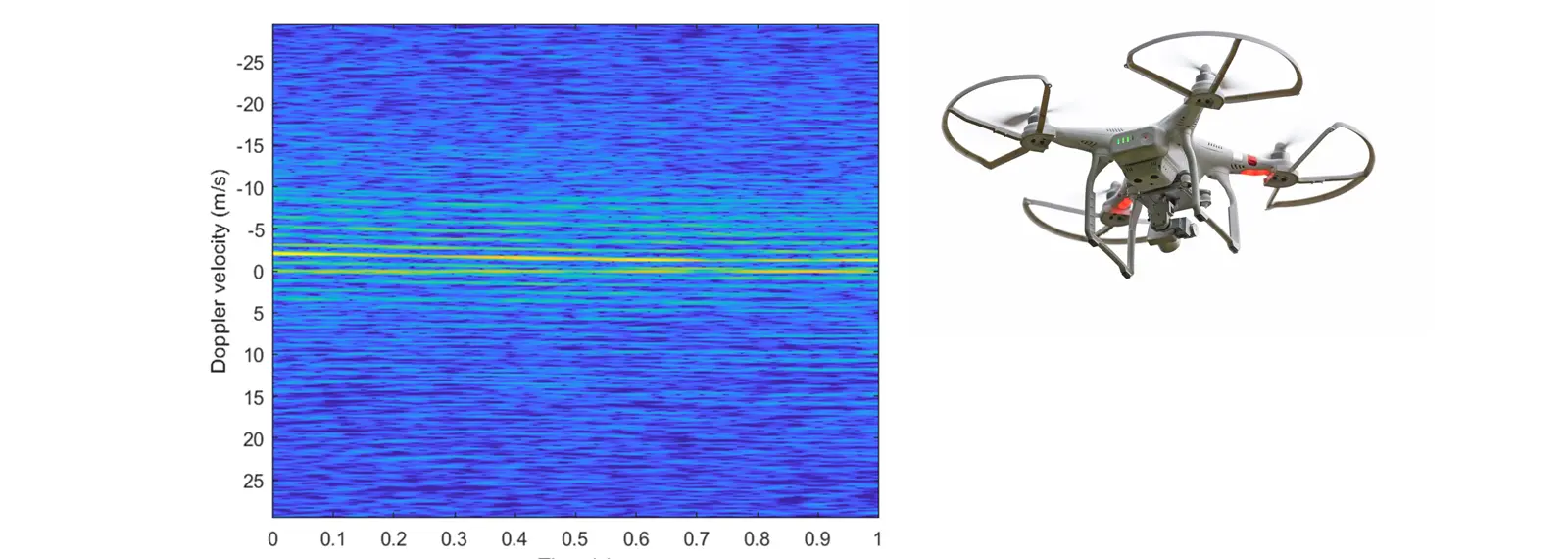
Target Classification: Drone
Target Classification
- Differentiate between drones and birds / other confusers
- Determine type of drone (e.g. fixed wing vs rotary wing)
- Estimate size of drone
Specification
-
Physical Size
Total (Inc Tx Mounting Bracket): 337 mm x 100 mm x 60 mm
-
Mass
Radar Module 1.4 kg
-
Supply Voltage
Input 12 – 15 VDC (regulated supply required)
-
Power Consumption
< 45 W
-
Transmit frequency
Within the allocation 15.7 – 17.2 GHz (Ku-band)
-
Transmit power
1 W typical (2 W max)
-
Transmission mode
FMCW
-
Beamforming
Beamform-on-receive using parallel receive channels
-
Transmitted bandwidth
20 MHz
-
Angular accuracy of detections (azimuth and elevation)
Typically ±3° or better
-
Detection Range
Target size dependent (Typically many hundreds of metres against a small target)
-
Field of view
120° (azimuth) x 20° (elevation).
Electronically-scanned on transmit concept to achieve 90° elevation Field of Regard (FoR)
-
Maximum instrumented range
800 m (Greater ranges attenuated by anti-alias filtering)
-
Range resolution
8 m
-
Data and Control Interface
GbE
-
IP Rating
Designed to meet IP65